Today more than ever businesses aim to work smarter and more efficiently, transforming their technology to best serve their business needs. There are many new technologies, tools and hyped buzzwords all claiming to bring value to your organization with a quick ROI.
Technologies such as Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and low-code development platforms are growing in popularity across the industry and even more so specifically in the SAP market. A critical part of selecting and implementing tools is understanding the differences between the different solutions, what will be the main benefits, and when to use one over the other. This is what we are here to explore in this blog.
ALL ABOUT ROBOTIC PROCESS AUTOMATION (RPA)
According to Gartner, by 2020 the RPA market was expected to reach $1 billion with 40% of large enterprises adopting the technology. Global Market Insights Inc. also says that the RPA market is expected to reach $5 billion by 2024.
But, what is RPA? When should you use it? Is it the right approach for you? How will it help your business and optimize operational efficiency, increase an existing process and optimize costs?
Let’s find out.
RPA is a form of business process automation technology based on the concept of self learning software robots. From logging into applications to moving files and folders, from copy & paste data to filling out forms, from extracting structured & semi-structured data from documents to scraping browsers - these virtual robots mimic many human user interactions with other software systems.
Mostly used in the back-office applications in industries such as insurance, banking, utilities, and telecommunications, RPA automates mechanical and routine tasks that don’t add much value but take a lot of time. It saves labor, time, and money by performing simple, repetitive tasks and helps businesses focus more on strategic and impactful activities.
When your approach to RPA is done right, you can benefit from it with -
- Reduced staffing costs and human error
- Increased scalability with a 24-hour virtual workforce
- Relatively low-cost implementation which saves more time
- Businesses are free from investing time in low-value-added tasks and focus on activities that really matter
- Quick productivity gains and potential for high ROI
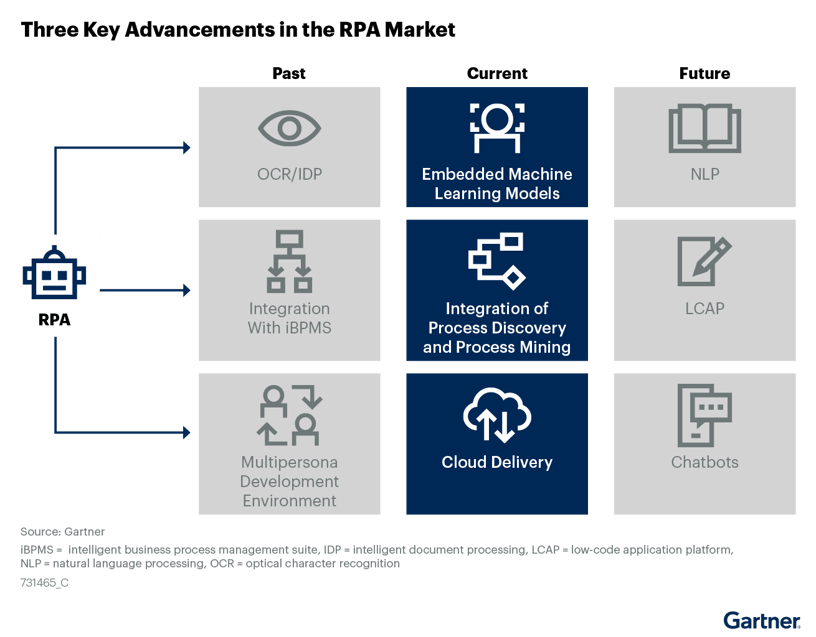
Below you can find Gartner's expected development in the RPA market
Low-code rapid application development platforms
A survey says that three-quarters of organizations will have at least four low-code solutions in their portfolio by 2024 and that’s huge!
But, what is low code? How is it different from RPA? Why is it the future of the digital economic age? What benefits can you get from it?
Let’s dive in and understand!
Today where time is money, low-code is a new approach to building unique business applications fast. As the name says, low-code requires very little coding to create an application (but still requires some coding skills as opposed to no-code solutions). Apps are not written line-by-line rather they are drawn like a flowchart often using a drag-and-drop approach which makes developing new applications quick and intuitive.
While companies are facing a shortage of skilled workers who have the necessary coding knowledge, specifically ABAP developers in the SAP market, low-code creates a bridge between the problem and business transformation. Using low-code, an individual or an enterprise with little to no coding knowledge can single-handedly design and build a complex business solution for their company at a fraction of the cost of hiring expensive developers or contracting an external firm to handle the design and development responsibilities.
While RPA covers the problems and acts as a band-aid by mimicking the repetitive and routine human user interactions with other software systems, low code can fix the issue at it's core by re-building the inefficient business process in the first place. This makes low code the surgeons’ scalpel solving the intricate problems. It fills the skill shortage gap, and allows business to focus on innovation and driving your organization forward.
Low-code development makes it easier than ever to create a flexible system to get specific tasks done. Some of low code's benefits are -
- In the long run, low-code helps organizations increase agility with less coding and automated testing
- It reduces the need for more developers, reducing hiring costs
- Low-code systems allow increased productivity by doing more work in less time and using the existing experienced developers to perform more advanced (and more interesting) work
- RPA is known to be rigid to innovation and changes whereas low-code makes changes and adaptation to new requirements easy
- Low-code simplifies building great, modern, and flexible business systems
With these low-code benefits, organizations are better equipped to quickly adapt and respond to fast-changing business conditions.
Read more on SAP Rapid Application Development.
So...RPA or low-code solutions - which will be better for my company?
RPA and low-code development platforms both are effective tools for effective Business Process Automation (BPA). Depending on the business and requirements, both RPA and low-code solutions are appropriate approaches for business automation in the world of the digital economic age.
The type of tool/platform approach that best solves your business problem depends on your situation. Each option can be a great or a bad fit, depending on the use case. Below is a table that summarizes each option and when to use each with its specific pros and cons.
|
RPA |
LOW-CODE |
|
|
USE-CASE |
|
|
|
PROS |
|
|
|
CONS |
|
|
TL;DR - Low-code and RPA are different
Though both RPA and low code have their own set of use-cases and bring their own pros and cons, with the increasing need for fast innovation - RPA’s fragility towards change is a major challenge for most organizations.
According to Gartner, more than 65% of application development in 2024 will be performed by low code platforms. By driving innovation and minimizing the time required to create and customize applications - low-code continues to become the new standard for business automation and transformation.
While RPA is robust software, it is not adaptive. Tiny changes in the business process or the underlying systems being used can make the whole automation process brittle requiring complete re-tuning. On the other hand, promising great potential and ROI to the business, low-code simplifies the engineering process and eases the restructuring of systems.
Understanding the requirements, a business can adapt the perfect approach for business automation. For companies that follow a routine process sans any little change and have a stable data format - RPA is well suited. But, for businesses looking for frequent innovation or require business agility – low code can prove to be a better, more sustainable approach.



 Back
Back/Logo%20-%20black%20text%20blue%20pillar%20(large)-1.jpg)

